A number of options are available for protecting the DNS server, including :
• DNS cache locking
• DNS socket pool
• DNSSEC
Before we start the step by step to implement the DNS Security, lets go through a theory behind this technology.
DNS Cache Locking
Cache locking
is a Windows Server 2016 security feature that allows you to control
when information in the DNS cache can be overwritten. When a recursive
DNS server responds to a query, it caches the results so that it can
respond quickly if it receives another query requesting the same
information. The period of time the DNS server keeps information in its
cache is determined by the Time to Live (TTL) value for a resource
record.
DNS Socket Pool
The DNS
socket pool enables a DNS server to use source port randomization when
it issues DNS queries. When the DNS service starts, the server chooses a
source port from a pool of sockets that are available for issuing
queries. Instead of using a predicable source port, the DNS server uses a
random port number that it selects from the DNS socket pool. The DNS
socket pool makes cache-tampering attacks more difficult because a
malicious user must correctly guess both the source port of a DNS query
and a random transaction ID to successfully run the attack. The DNS
socket pool is enabled by default in Windows Server 2016
DNSSEC
DNSSEC
enables a DNS zone and all records in the zone to be signed
cryptographically so that client computers can validate the DNS
response. DNS is often subject to various attacks, such as spoofing
and cache-tampering. DNSSEC helps protect against these threats and
provides a more secure DNS infrastructure.
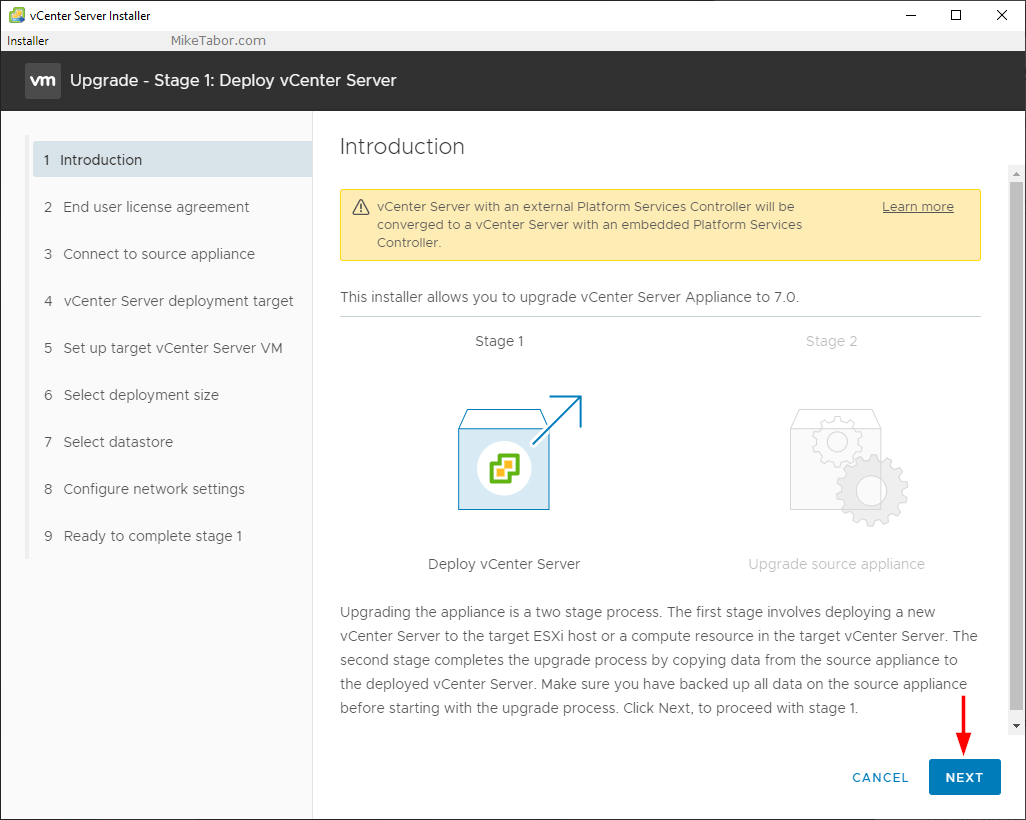
So now, lets go through a simple step how you as Server Administrator can implement DNS Security.
01 – Step to configure DNSSEC
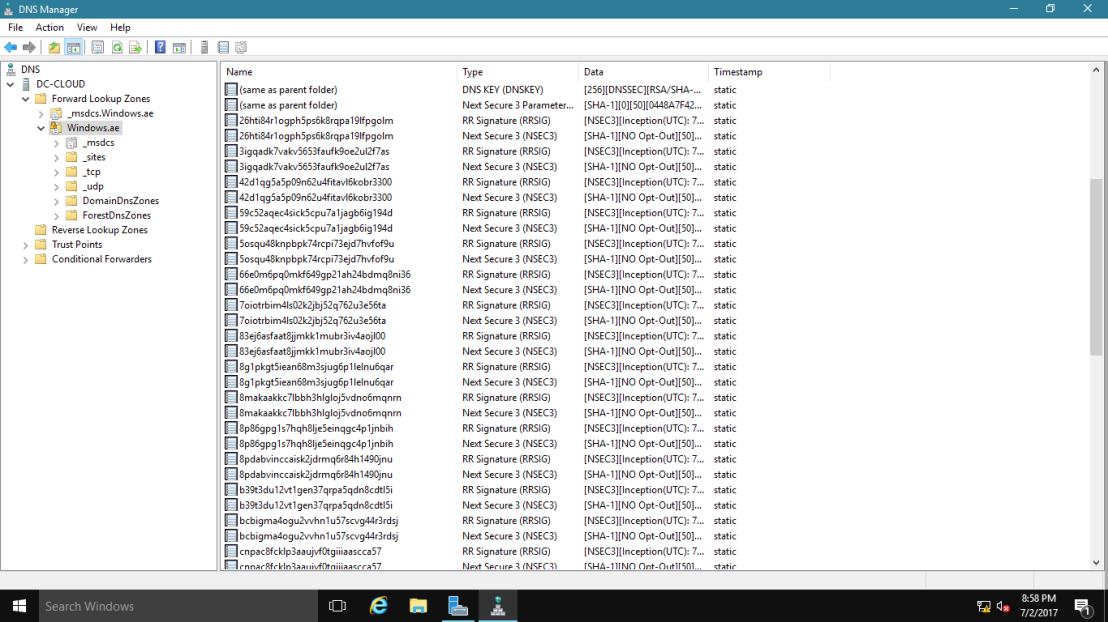
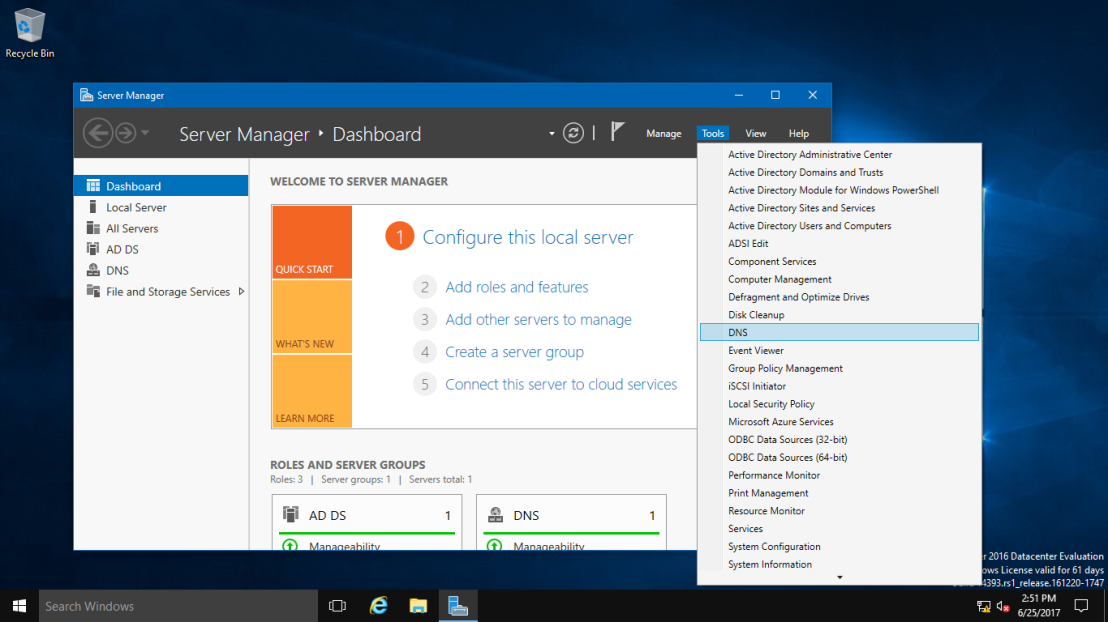
1 – Open Server Manager, click Tools and open DNS Manager.
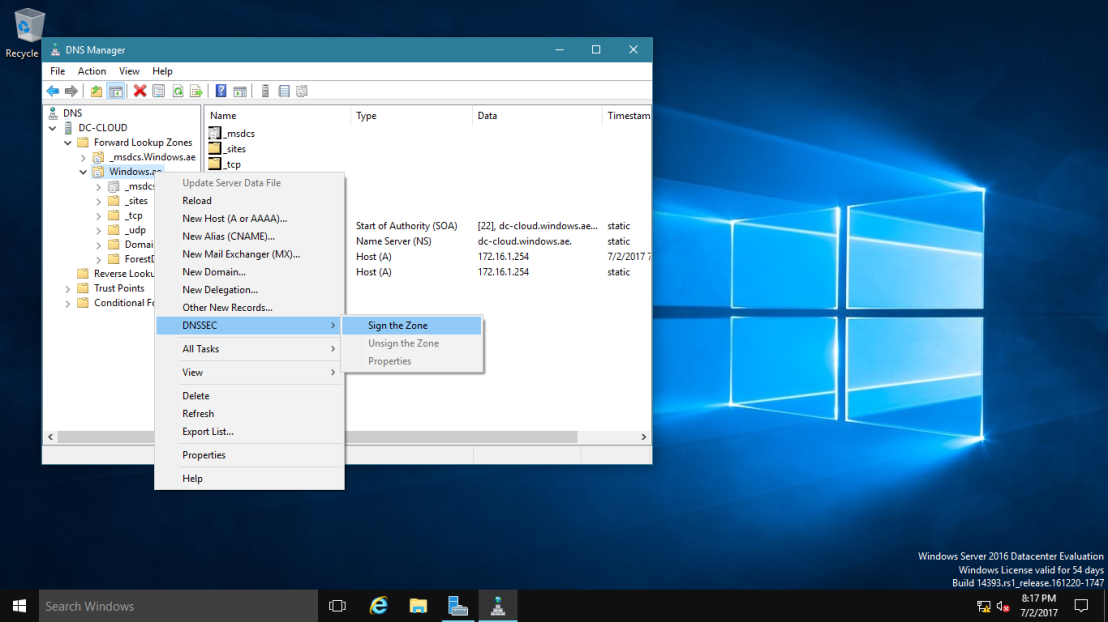
2 – In the DNS Manager, browse to your Domain name, then right click domain name, click DNSSEC and then click Sign the Zone.
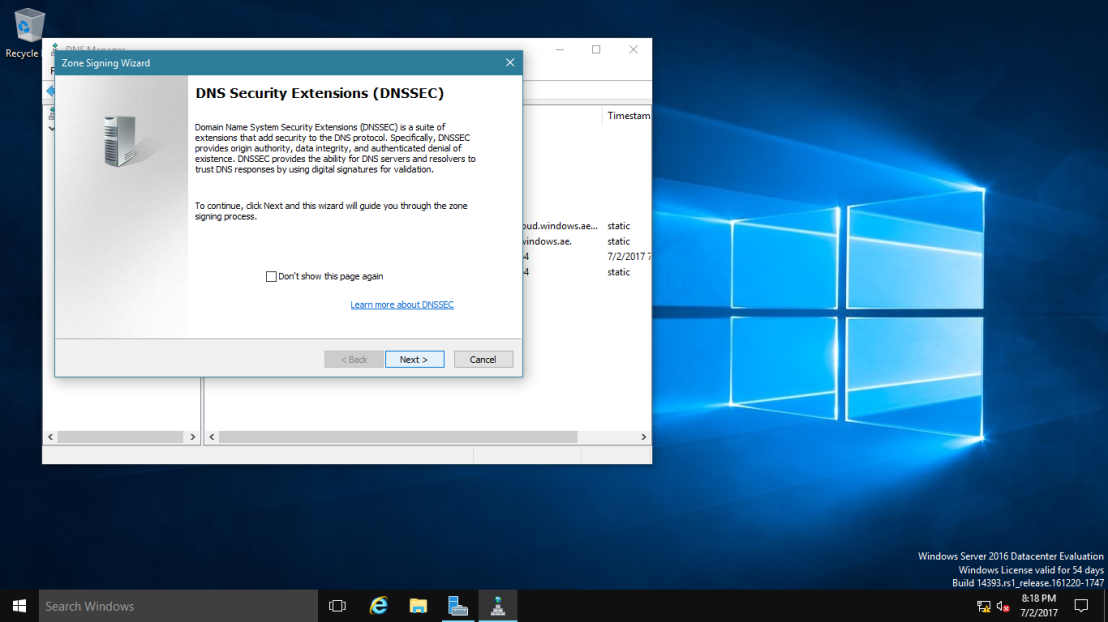
2 – In the Zone Signing Wizard interface, click Next.
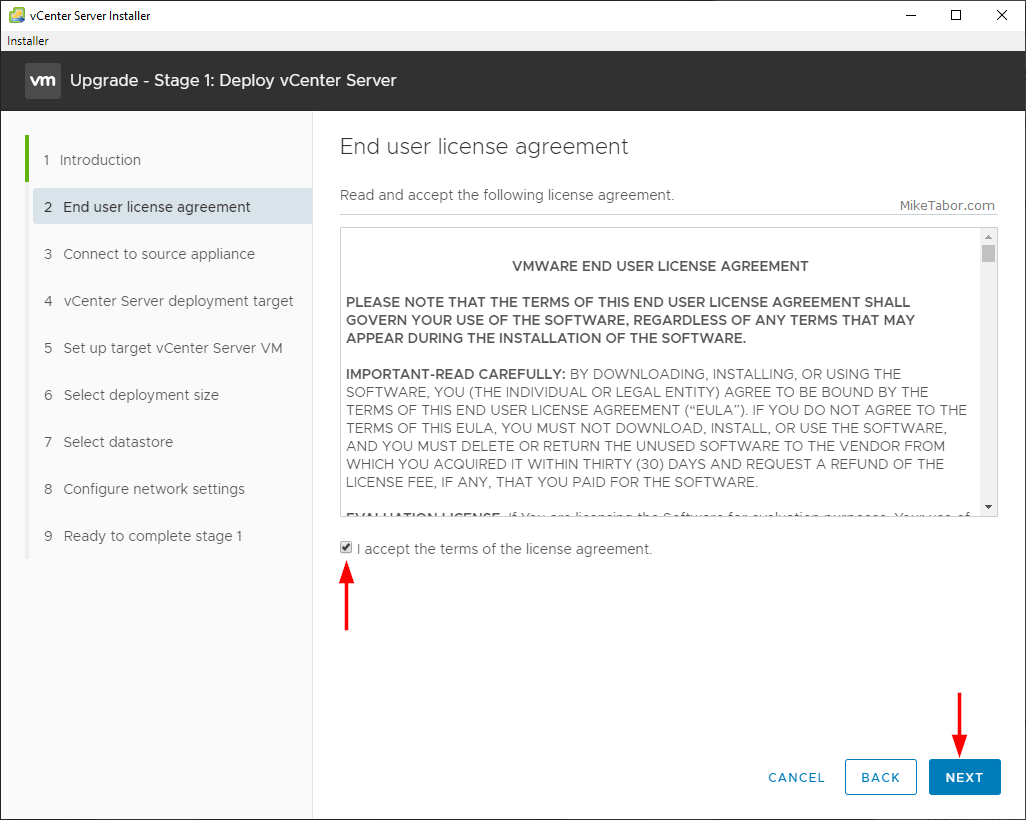
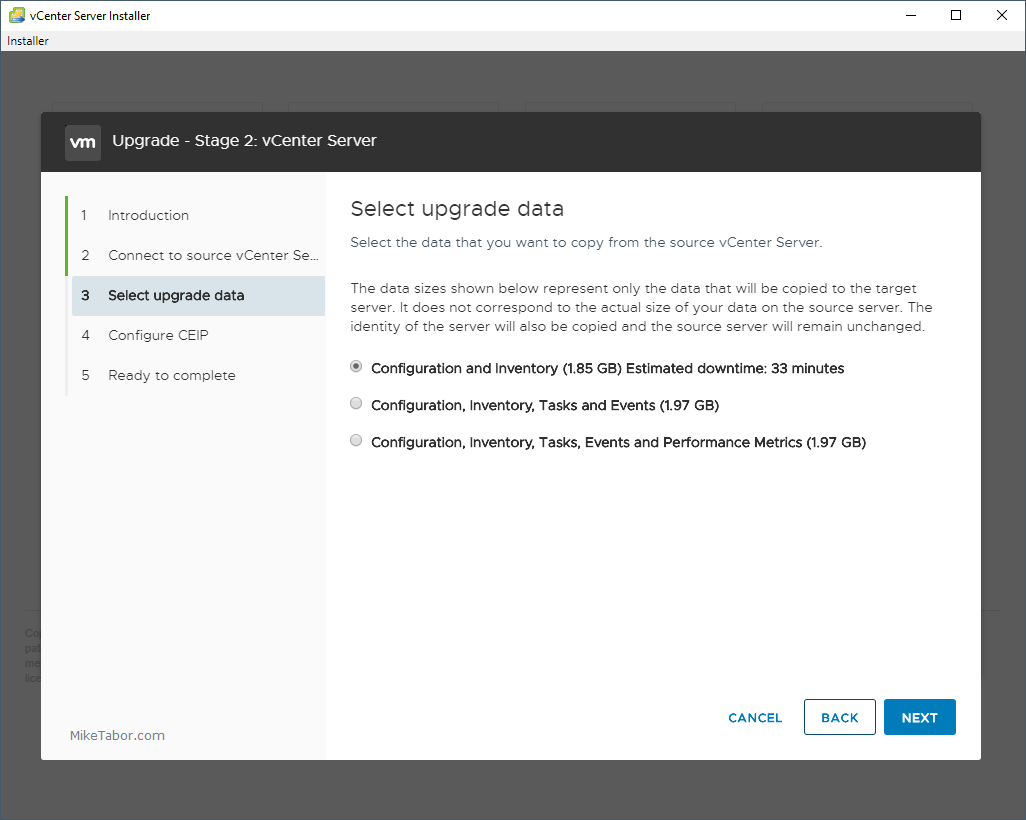
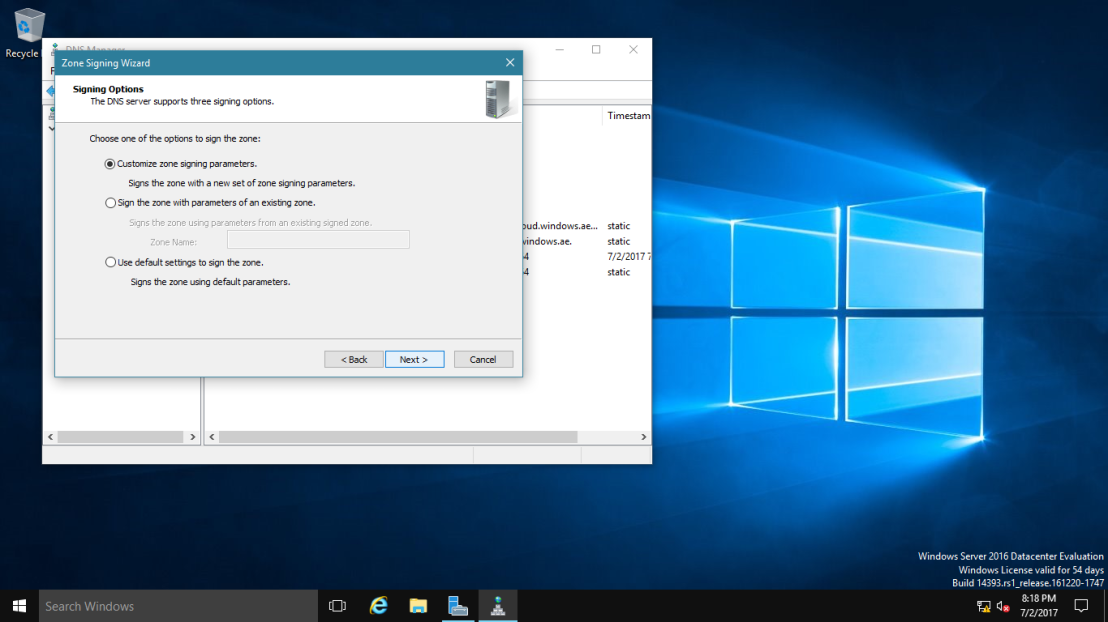
3 – On the Signing options interface, click Customize zone signing parameters, and then click Next.
4 – On the Key Master interface, ensure that “The DNS server CLOUD-SERVER is selected as the Key Master“, and then click Next.
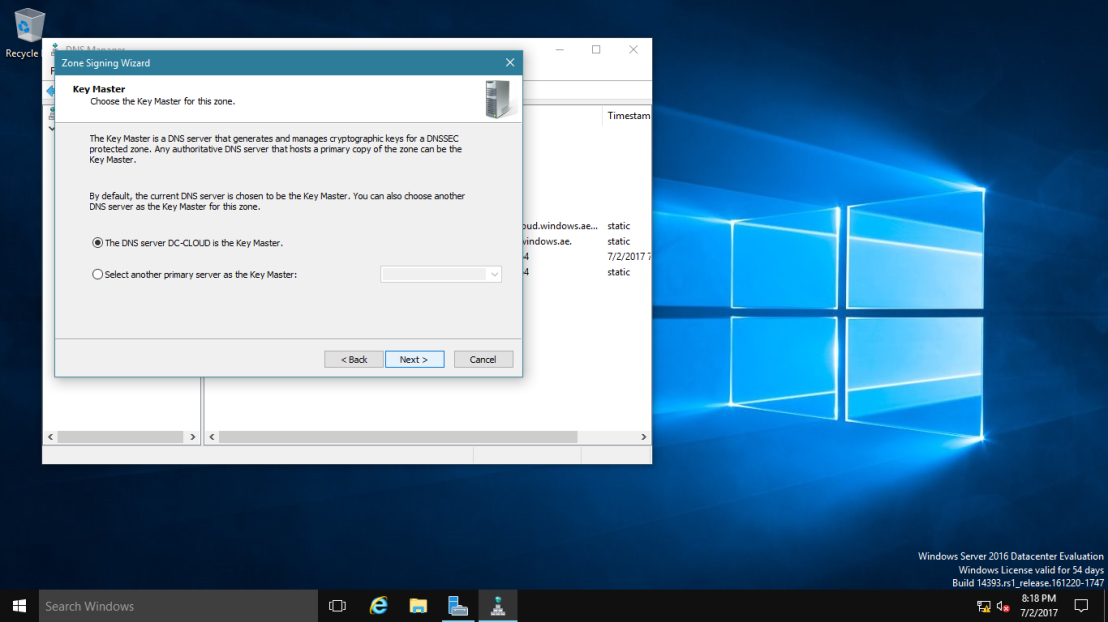
5 – On the Key Signing Key (KSK) interface, click Next.
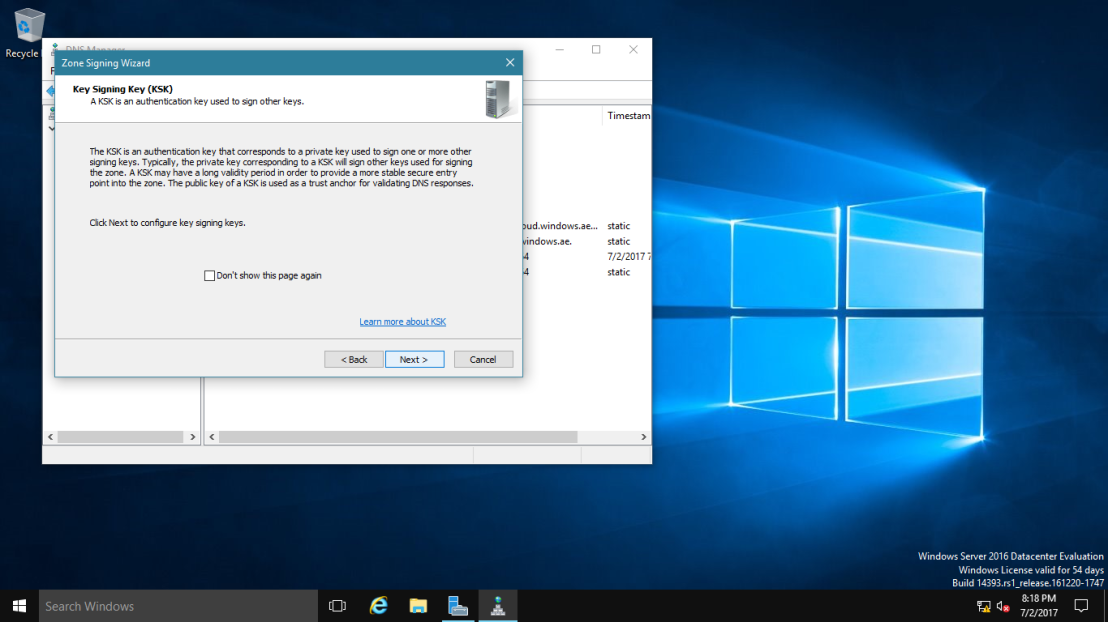
6 – On the Key Signing Key (KSK) interface, click Add.
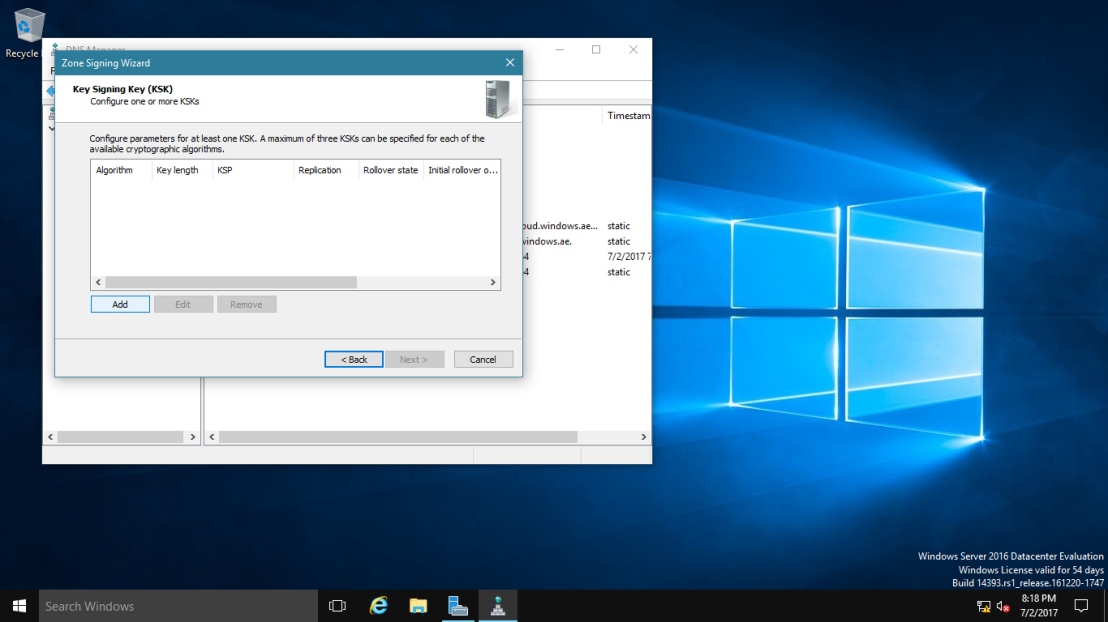
7 – On the New Key Signing Key (KSK) interface, click OK.
~*~ please spend some time to go through about key properties on the New Key Signing Key (KSK) interface.
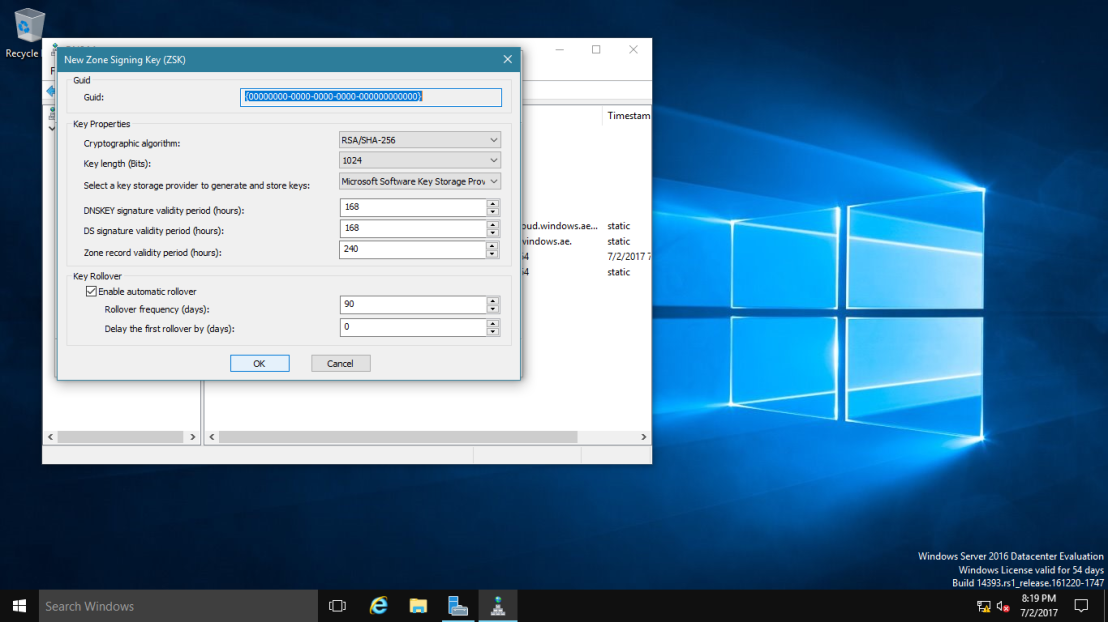
8 – On the Key Signing Key (KSK) interface, click Next.
9 – On the Zone Signing Key (ZSK) interface, click Next.
10 – On the Zone Signing Key (ZSK) interface, click Add.
11 – On the New Zone Signing Key (ZSK) interface, click OK.
12 – On the Zone Signing Key (ZSK) interface, click Next.
13 – On the Next Secure (NSEC) interface, click Next.
~*~ NSEC is when the DNS response has no data to provide to the client, this record authenticates that the host does not exist.
14 – On the Trust Anchors (TAs) interface, check the Enable the distribution of trust anchors for this zone check box, and then click Next.
~*~ A trust anchor is an authoritative entity that is represented by a public key. The TrustAnchors zone stores preconfigured public keys that are associated with a specific zone.
15 – On the Signing and Polling Parameters interface, click Next.
16 – On the DNS Security Extensions (DNSSEC) interface, click Next, and then click Finish.
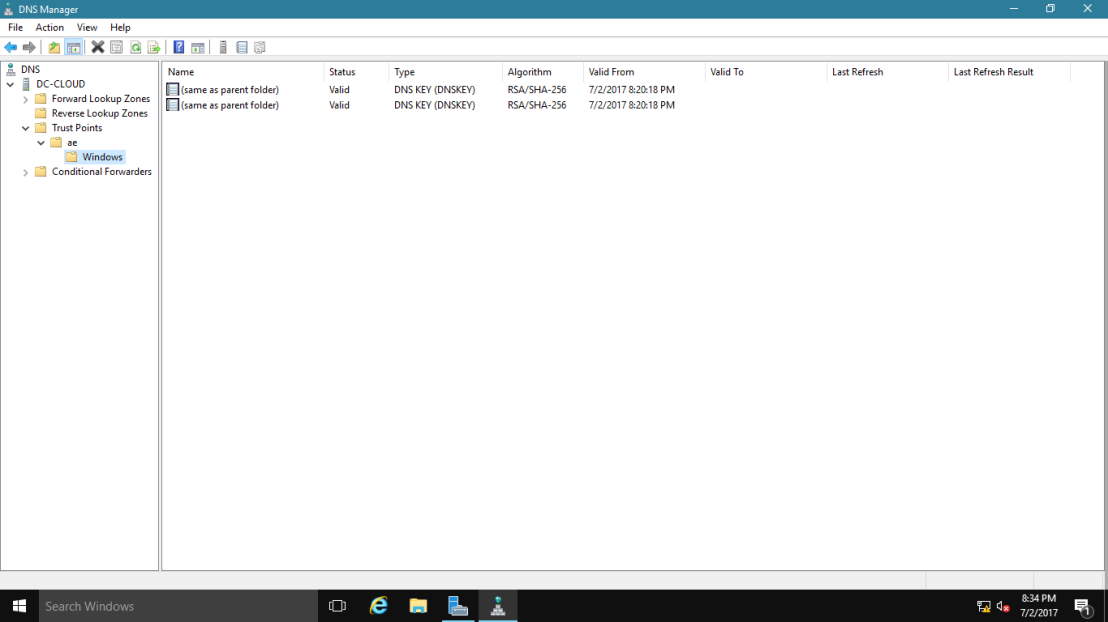
17 – In the DNS console, expand Trust Points, expand ae, and then click your domain name.
Ensure that the DNSKEY resource records display, and that their status is valid.
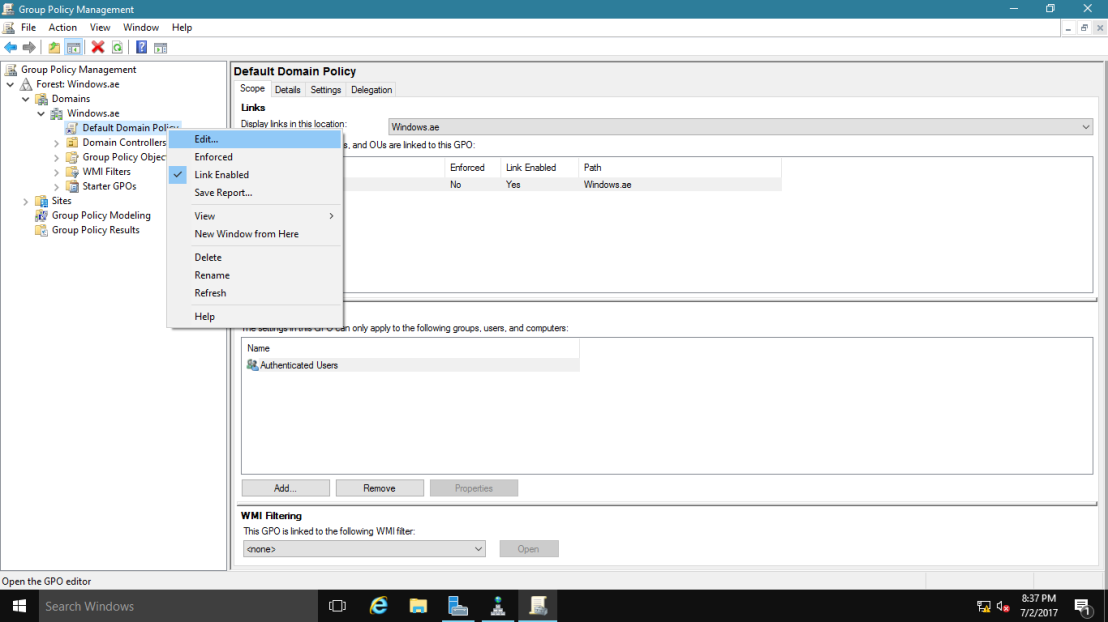
18 – Open Server Manager, click Tools and open Group Policy Management.

19 – Next, open Group Policy Management, expand Forest: Windows.ae, expand Domains, expand Windows.ae, right-click Default Domain Policy, and then click Edit.
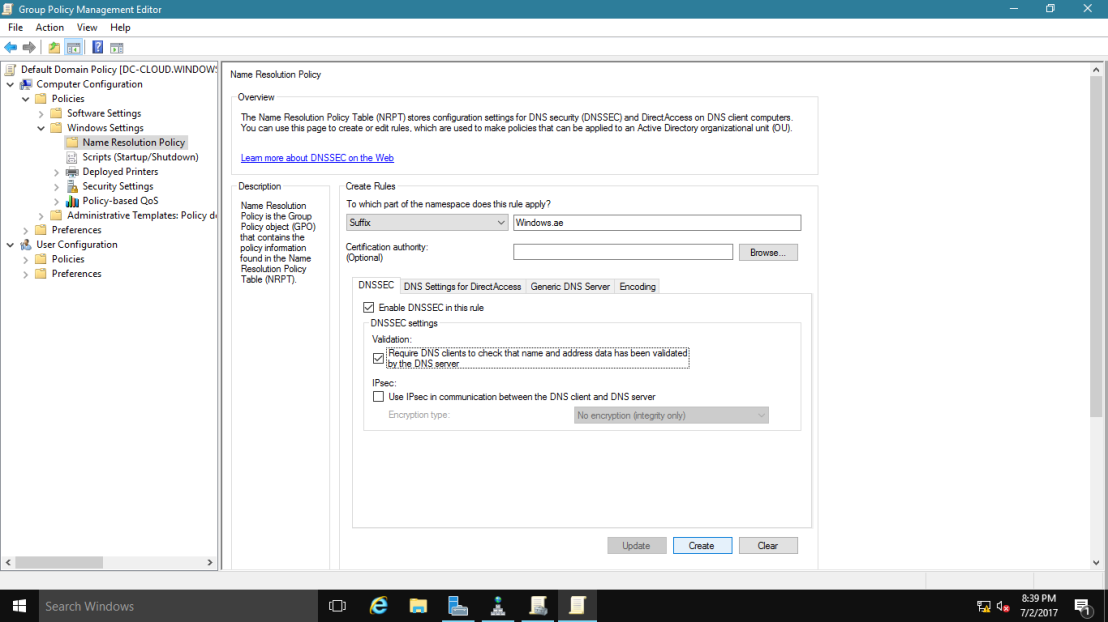
20 – In the Group Policy Management Editor interface, under Computer Configuration, expand Policies, expand Windows Settings, and then click Name Resolution Policy.
~*~ In the right pane, under Create Rules, in the Suffix box, type Windows.ae to apply the rule to the suffix of the namespace.
~*~ Select both the Enable DNSSEC in this rule check box and the Require DNS clients to check that the name and address data has been validated by the DNS server check box, and then click Create.
02 – Configure the DNS Socket Pool
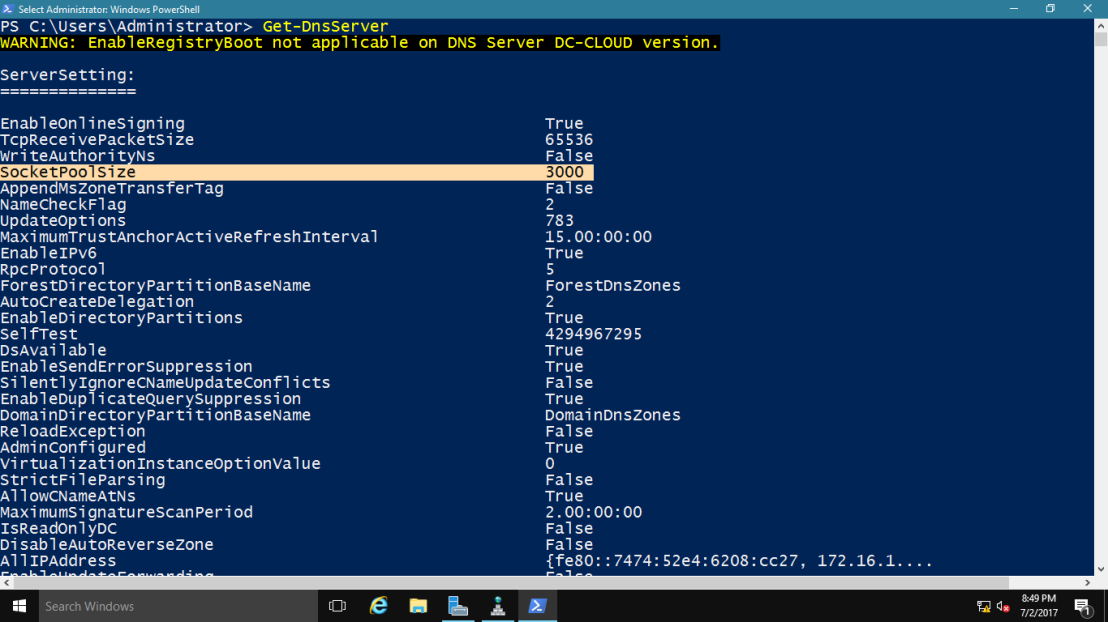
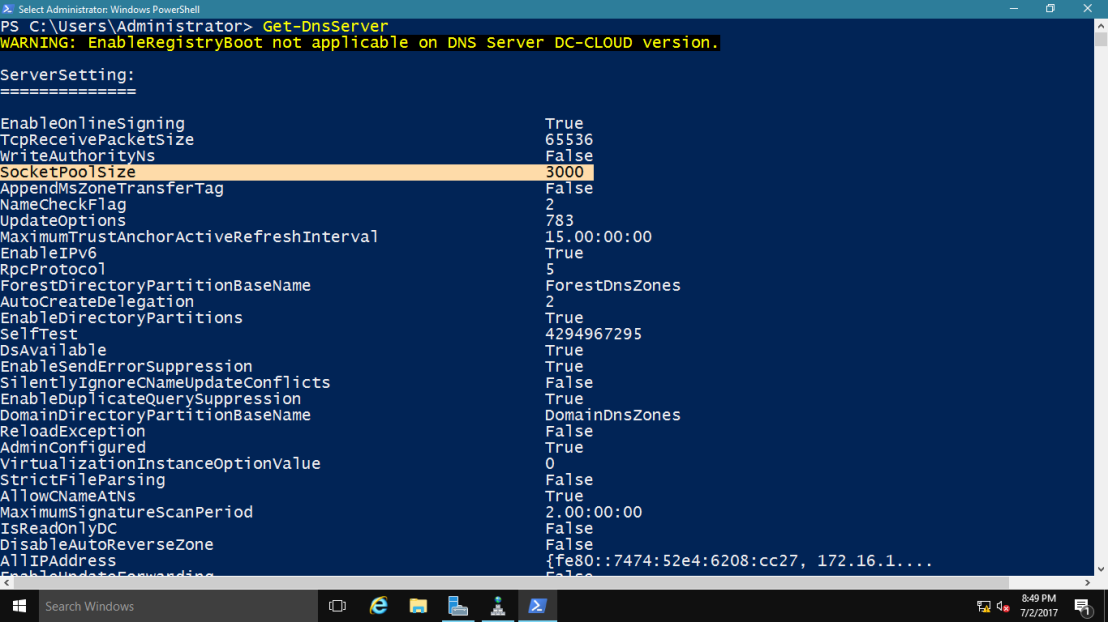
1 – In domain Server, open Windows PowerShell and type : Get-DNSServer
~*~
This command displays the current size of the DNS socket pool (on the
fourth line in the ServerSetting section). Note that the current size is
2,500.
~*~ Please
take note that the default DNS socket pool size is 2,500. When you
configure the DNS socket pool, you can choose a size value from 0 to
10,000. The larger the value, the greater the protection you will have
against DNS spoofing attacks.

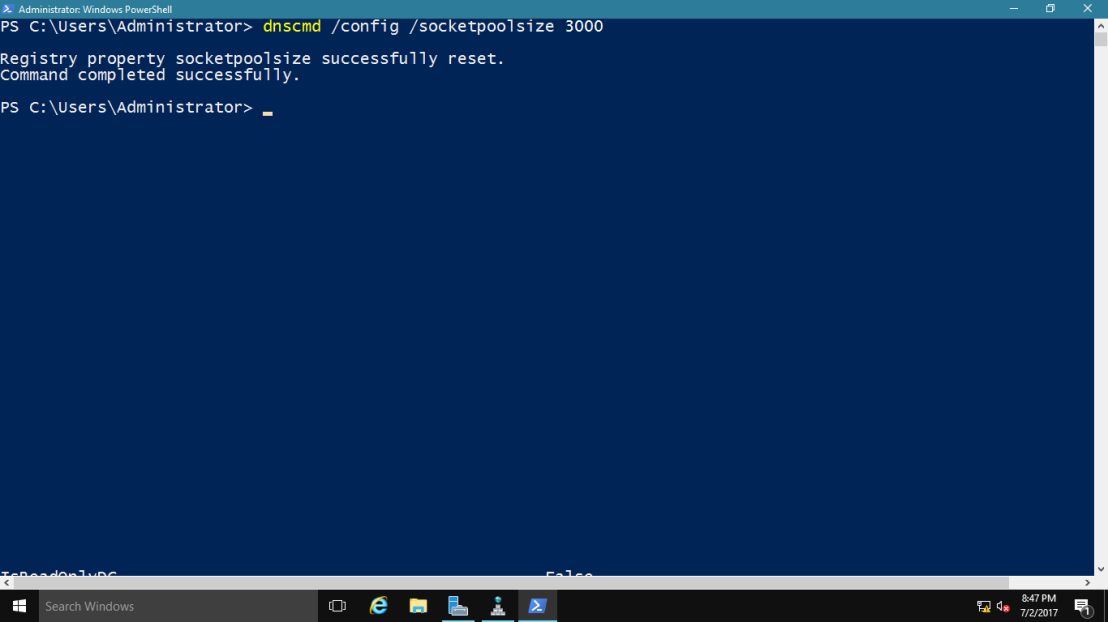
2 – Now lets change the socket pool size to 3,000.
type : dnscmd /config /socketpoolsize 3000
3 – Restart your DNS Server for the changes to take effect.
~*~ confirm that the new socket pool size now is 3000
04 – Configure the DNS Cache Locking
1 – In Windows PowerShell, type Get-Dnsserver
~*~ This command will displays the current percentage value of the DNS cache lock.
~*~ Note that the current value is 100 percent.
2 – type Set-DnsServerCache –LockingPercent 70
~*~ This changes the cache lock value to 70 percent
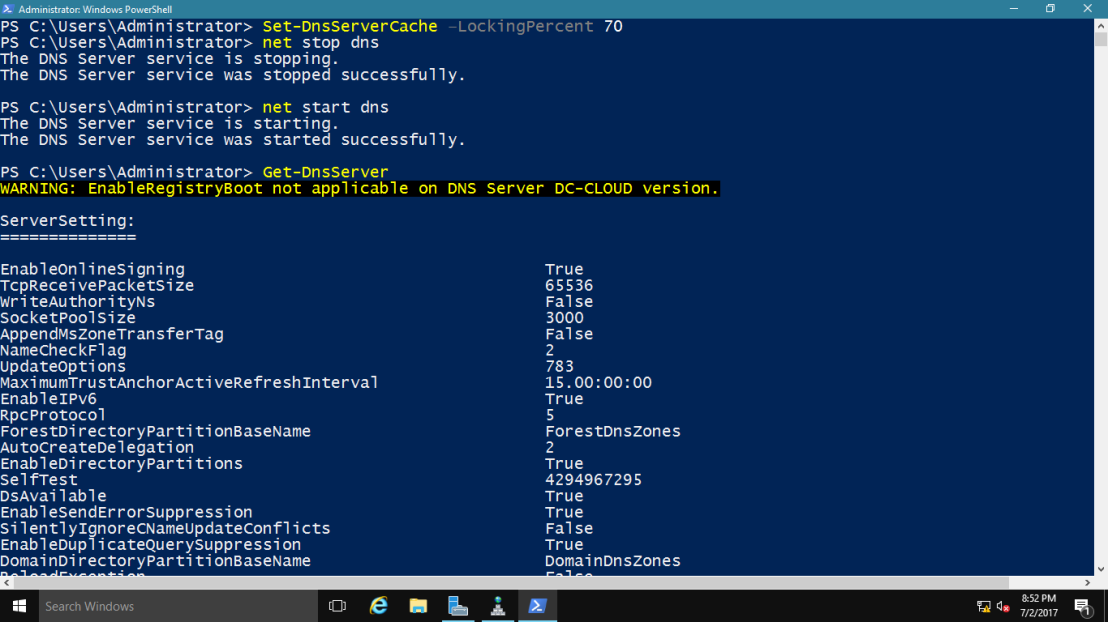
~*~ Please take note that you configure cache locking as a percentage value.
3 – Looking your DNS Manager Verify.