Cybercriminals are hungry for passwords. As seen in plenty of news articles about hacks and data leaks, an unprotected password can help cybercriminals gain access to your bank account, credit cards, or personal websites. From there, they can sell your personal information, gain access to your money, or compromise your overall digital security.
But the battle isn’t lost. One way to quickly boost the safety of your online accounts is two-factor authentication — also known as 2FA — which adds an extra layer of security to your accounts.

What is 2FA?
Two-factor authentication (2FA) is an extra step added to the log-in process, such as a code sent to your phone or a fingerprint scan, that helps verify your identity and prevent cybercriminals from accessing your private information. 2FA offers an extra level of security that cyberthieves can’t easily access, because the criminal needs more than just your username and password credentials.
2FA is a subset of multi-factor authentication, an electronic authentication method that requires a user to prove their identity in multiple ways before they are allowed access to an account. Two-factor authentication is so named because it requires a combination of two factors, whereas multi-factor authentication can require more.
A good example of two-factor authentication in the real world is an ATM card. In addition to physically presenting the card, you also need to type in your PIN to access your account.
On the web, you can find examples of 2FA just by taking a scroll through your browser history. You’ll find plenty of websites where all you need is your username or email and your password. These use one-factor authentication, where the password is the only thing you need for entry.
As the name suggests, two-factor authentication requires one extra step — and a second factor — to log onto a site or access an online account. Most often, you first enter your username and password. The site typically then sends a text message to your mobile phone with a six-digit numerical code. This code is called an authenticator, or sometimes a passcode or verification code. You can only access the site by then entering this code that appears on your mobile device. If you don't have the code, you can't log on, even if you know the correct password.

Why do I need 2FA?
Passwords are historically weak, due to both the advanced nature of hacking and a general annoyance with password creation and use. A Harris Poll found that 78% of Gen Z uses the same password across multiple accounts, increasing their overall vulnerability if a criminal was to figure out their credentials. And beyond that: About 23 million accounts still use the password “123456.”
With it becoming increasingly easy for cybercriminals to guess passwords, 2FA is more important than ever. It might seem like a hassle to add an extra step to your web surfing, but without it you could be leaving yourself vulnerable to cybercriminals who want to steal your personal information, access your bank accounts, or hack into your online credit card portals.
Adding the extra step to account access means thieves will struggle to access your personal information. If you add a knowledge factor to your bank account, a cybercriminal who knows your password won’t be able to access the account without having your phone when it receives the verification code.
That way, those still relying on the password “password” have a better shot at keeping their bank accounts secure.
How 2FA works
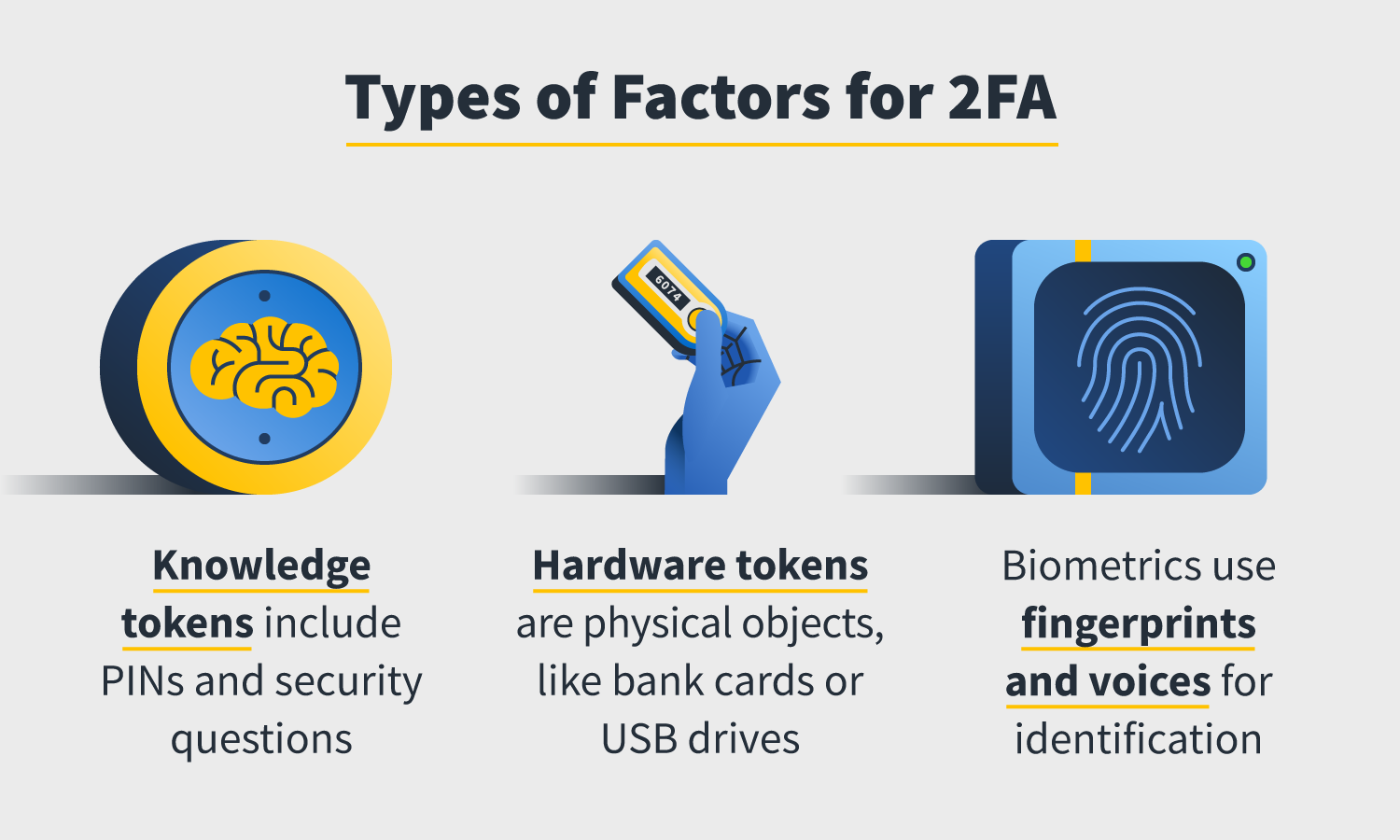
To understand two-factor authentication, you first need to understand factors. A 2FA factor is what you will need to access the account, and they are generally broken into three categories:
- Knowledge: These factors require you to know something, like security questions, a PIN sent to your device, or a specific keystroke.
- Possession: The user must physically possess the factor, like a debit card or a USB drive, and insert it into the device to gain entry.
- Biology: Access is granted once the user proves their identity through biological markers like a fingerprint or voice.
Types of 2FA
There are several types of 2FA available, all of them relying on the different forms of factors we’ve listed above.
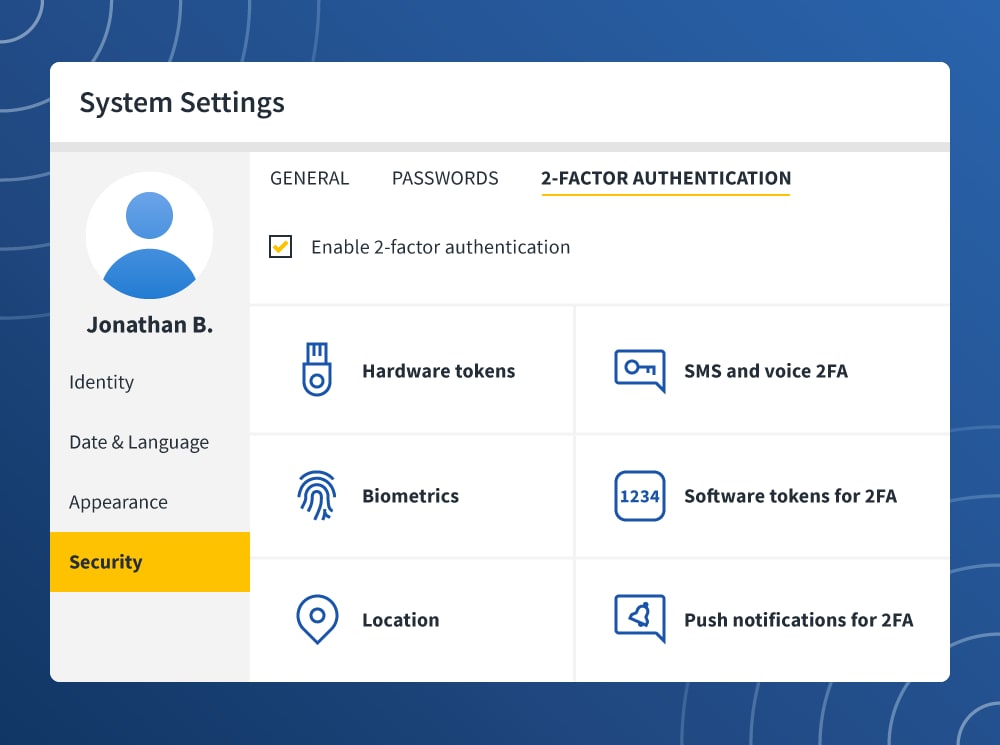
- Hardware tokens: This type of 2FA requires users to possess a type of physical token, such as a USB token, that they must insert in their device before logging on. Some hardware tokens display a digital code that users must enter.
- SMS and voice 2FA: You’ll receive either a text or voice message giving you a code that you must then enter to access a site or account.
- Software tokens for 2FA: These tokens are apps that you download. Any site that features 2FA, will then send a code to the app that you enter before logging on.
- Push notifications for 2FA: You’ll download a push notification app to your phone. When you enter your login credentials to access a website, a push notification is sent to your smartphone. A message will then appear on your phone requesting that you approve your log-in attempt with a tap.
- Biometrics: To log onto a site, you’ll first have to verify it’s you through something physical about yourself. Most commonly, this means using a fingerprint scanner.
- Location: If your account was created and registered in one state, and suddenly a log-in is attempted in a different location, it may trigger a location factor. These factors will alert you when a log-in is attempted on a new device and send you a code to enter to verify your identity.
How to enable 2FA
Though not all sites use 2FA, some give you the option to activate it for your account. For sites that enable 2FA, you can find the toggle to turn it on in your settings, usually under the Security tab.
Some popular websites that do enable 2FA include: Amazon, Facebook, Instagram, Dropbox, Lastpass, LinkedIn, Intuit, TurboTax, Mint, PayPal ,and Yahoo. For a complete list of websites that have 2FA capabilities, visit this website.
Adding two-factor authentication to your high-priority accounts can help keep you — and your money and personal information — more secure.
How secure is 2FA?
A harsh reality: Nothing is 100 percent secure. There are ways that criminals can bypass the system and access your account even if you have 2FA enabled. For example, lost password recovery usually resets your password via email, and it can completely bypass 2FA.
However, adding an extra roadblock for cybercriminals looking to access your accounts is better than taking a chance and leaving yourself vulnerable by not enabling 2FA.

best wine racks
ReplyDeleteLenovo V15 Laptop
ReplyDeleteMobile Phone
ReplyDeleteOPPO Mobile Phone
Find X2 Pro 5G
5G download speeds
Tech To Learn
ReplyDeleteTech To Learn
Tech To Learn
Tech To Learn
Tech To Learn
Tech To Learn
Tech To Learn
Tech To Learn
Tech To Learn
Tech To Learn
Tech To Learn
Tech To Learn
Tech To Learn
Tech To Learn
Tech To Learn
Tech To Learn
Tech To Learn
Tech To Learn
Tech To Learn
Tech To Learn
Tech To Learn
Tech To Learn
Tech To Learn
Tech To Learn
Tech To Learn
Tech To Learn
Tech To Learn