For our example, we have a two node cluster based on the Windows
Server 2012 R2 operating system where we will be installing SQL Server
2014. The name of the nodes are SQL-NODE1 and SQL-NODE2. We need a
unique and unused IP address and SQL Server Network Name to complete
this installation. We will use MSSQLCLUSTER as the network name and the
IP address 10.2XX.XX2.1X. (note: X represents a numeric value, I put X
because I do not want to disclose my IP address due to security
reasons). So let's start the SQL Server installation on node SQL-NODE1.
Before we begin, make sure the cluster resources (like the shared
drives) are accessible by SQL-NODE1.
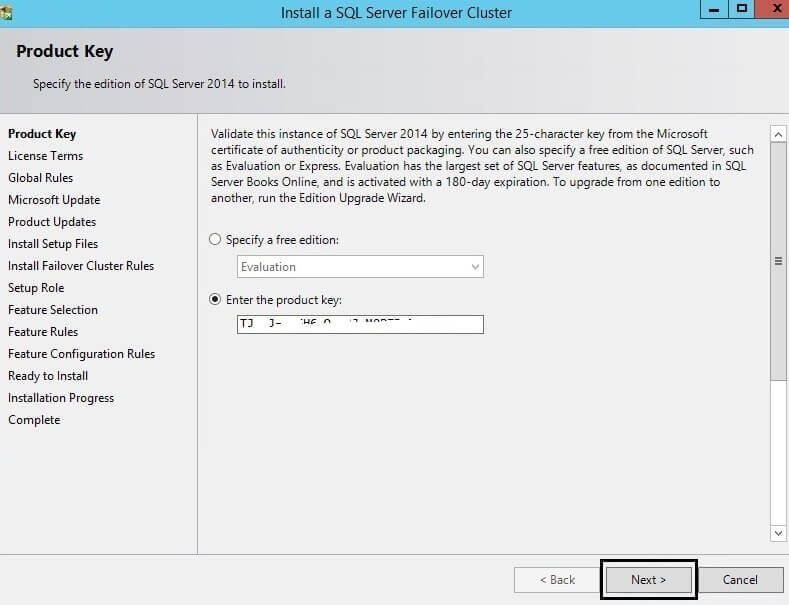
 Step 2: Once you click on "New SQL Server failover cluster
installation", the SQL Server installation window will appear and it
will ask you to enter your product key for SQL Server. Enter the key or
if it is an evaluation version choose the first option. Sometimes the
product key option will be grayed out, so in that case you can just
click the Next button.
Step 2: Once you click on "New SQL Server failover cluster
installation", the SQL Server installation window will appear and it
will ask you to enter your product key for SQL Server. Enter the key or
if it is an evaluation version choose the first option. Sometimes the
product key option will be grayed out, so in that case you can just
click the Next button.
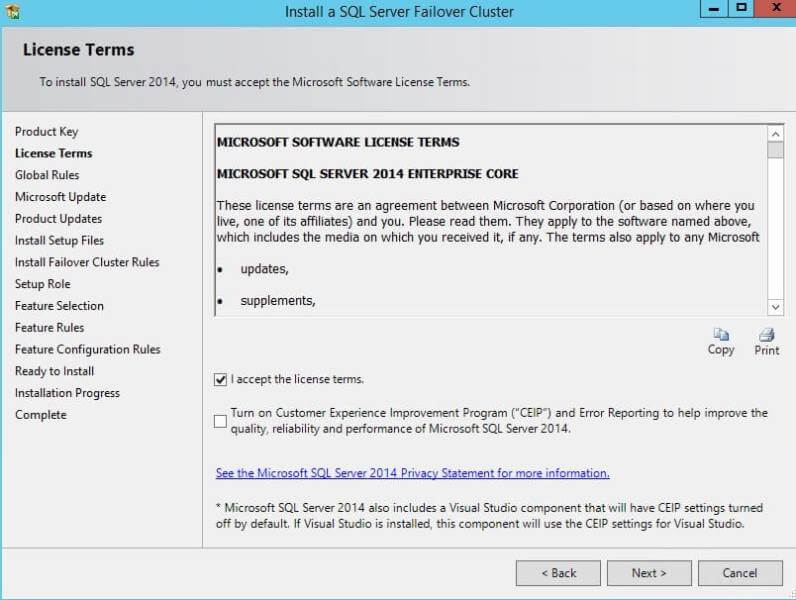
 Once you click on Next, another window will load and ask you to click
on the check box to accept the license terms and conditions for the SQL
Server product. Click on the Next button after accepting the license
terms.
Once you click on Next, another window will load and ask you to click
on the check box to accept the license terms and conditions for the SQL
Server product. Click on the Next button after accepting the license
terms.
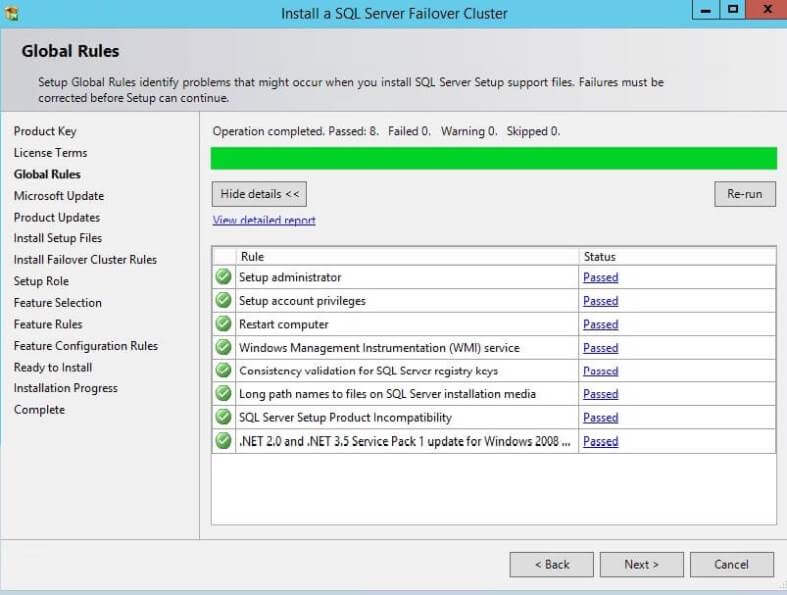
 Step 3: After accepting the license terms, SQL Server will
start checking the global rules and display the status of all the rules.
If any rule fails, setup will not proceed further and you need to first
fix the issue. You can see below the rules are successful, so click on
the Next button to proceed.
Step 3: After accepting the license terms, SQL Server will
start checking the global rules and display the status of all the rules.
If any rule fails, setup will not proceed further and you need to first
fix the issue. You can see below the rules are successful, so click on
the Next button to proceed.
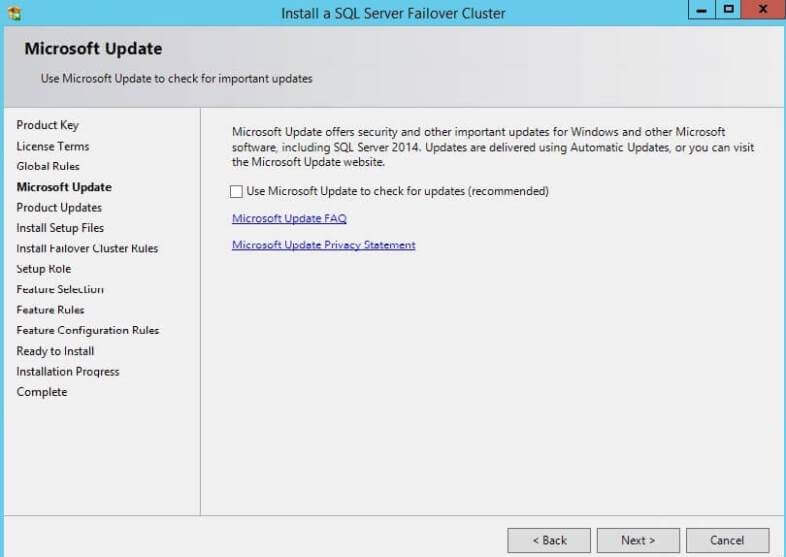
 Step 4: The next window will ask you to check for Microsoft
Updates for Windows and SQL Server 2014. I have not checked this option,
but if you want to check for updates from Microsoft you can click on
the check box in the below screenshot.
Step 4: The next window will ask you to check for Microsoft
Updates for Windows and SQL Server 2014. I have not checked this option,
but if you want to check for updates from Microsoft you can click on
the check box in the below screenshot.
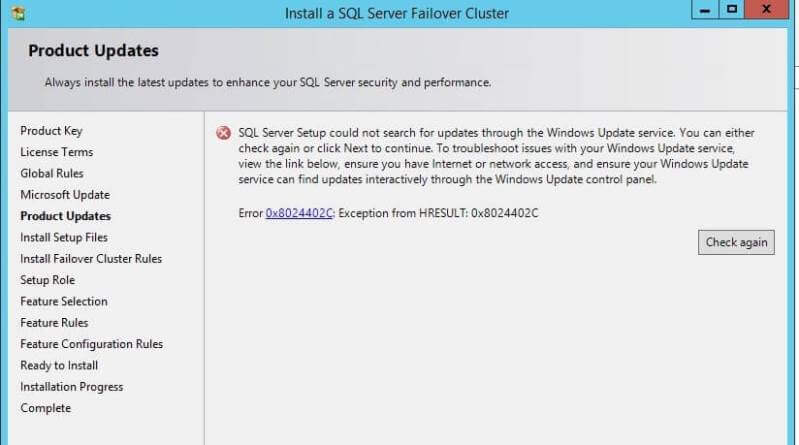
 Once you click on the Next button of the above screen, the Product
Update window will appear. As I have not chosen Microsoft updates in
last window, the error is indicating that "SQL Server could not search
for updates..." as shown in the below screenshot. Click on the Next
button to proceed.
Once you click on the Next button of the above screen, the Product
Update window will appear. As I have not chosen Microsoft updates in
last window, the error is indicating that "SQL Server could not search
for updates..." as shown in the below screenshot. Click on the Next
button to proceed.
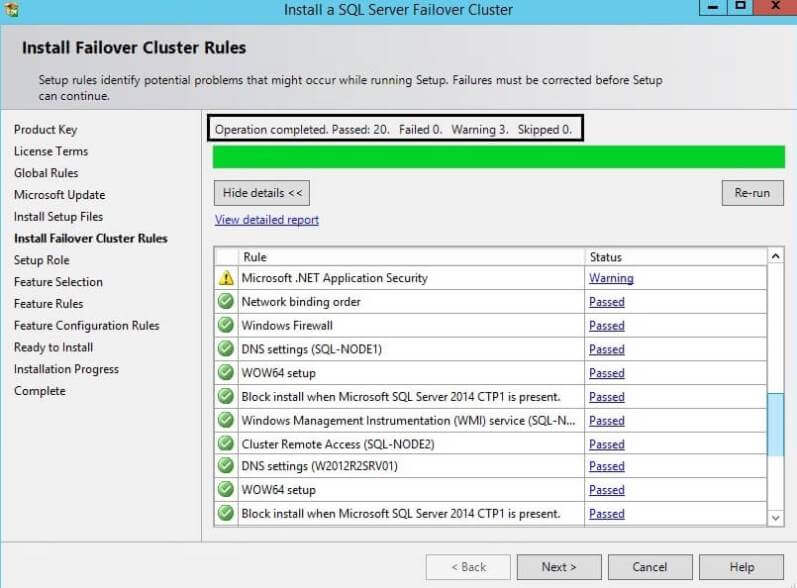
 Step 5: The next window will check failover cluster rules. We
can see all rules have been checked with both successful and warning
results. We can skip warnings at this point in time as we can fix them
post installation. Click on the Next button to proceed with the
installation.
Step 5: The next window will check failover cluster rules. We
can see all rules have been checked with both successful and warning
results. We can skip warnings at this point in time as we can fix them
post installation. Click on the Next button to proceed with the
installation.
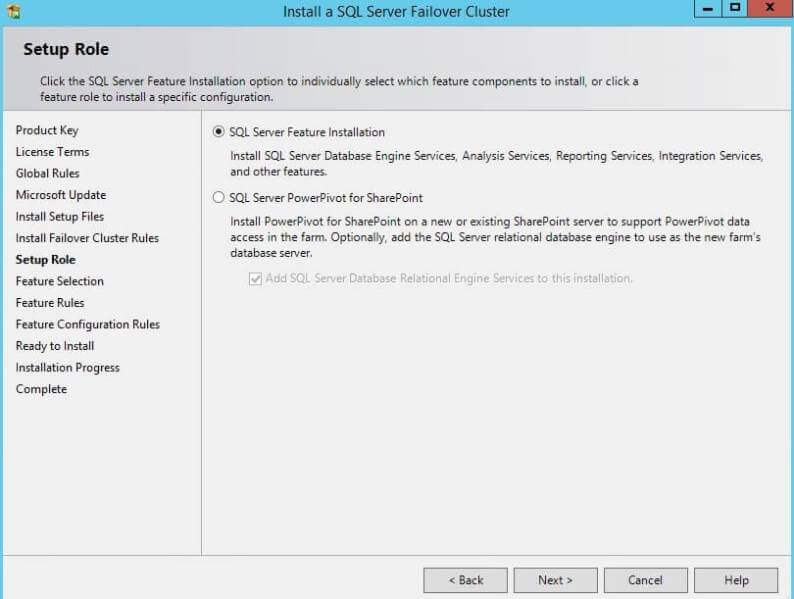
 Step 6: The next interface is the setup role window, where you
choose the installation features. You will find two options on this
page. One is to configure SQL Server feature installation and another is
to configure SQL Server PowerPivot for SharePoint. Since I have to
install the SQL Server database engine, I will choose the first option.
Once you choose your setup role, click on the Next button.
Step 6: The next interface is the setup role window, where you
choose the installation features. You will find two options on this
page. One is to configure SQL Server feature installation and another is
to configure SQL Server PowerPivot for SharePoint. Since I have to
install the SQL Server database engine, I will choose the first option.
Once you choose your setup role, click on the Next button.
 Step 7: The next step in the process is for feature selection.
Choose the features you want to install on your cluster server. Do not
select all features if you will not use them, as this will use server
resources that could be used by the SQL Server database engine or
Windows. I have selected the SQL Server Database Engine along with a few
shared features as shown in the below screenshot. You can also change
the root directory for each of the selected features and for the SQL
Server binaries.
Step 7: The next step in the process is for feature selection.
Choose the features you want to install on your cluster server. Do not
select all features if you will not use them, as this will use server
resources that could be used by the SQL Server database engine or
Windows. I have selected the SQL Server Database Engine along with a few
shared features as shown in the below screenshot. You can also change
the root directory for each of the selected features and for the SQL
Server binaries.
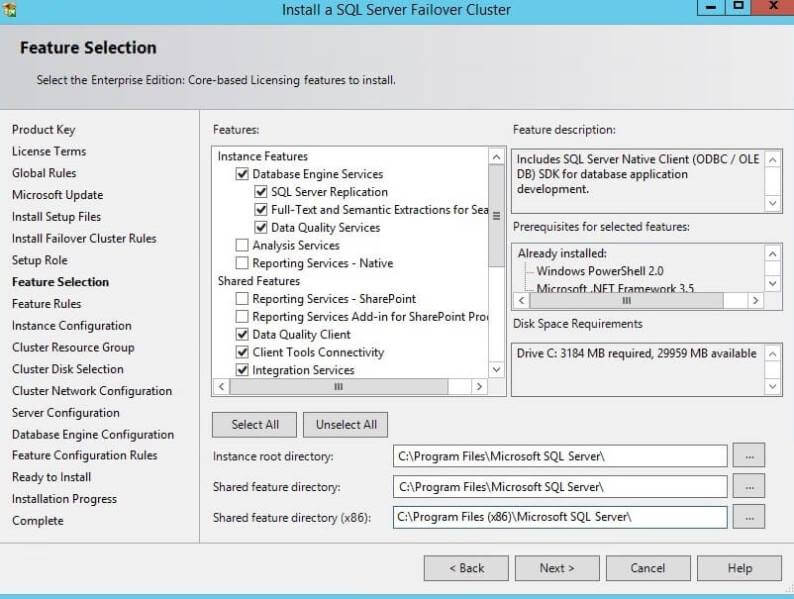 Click the Next button after selecting the features you want to
install. Another window will check the feature rules. Once every rule is
checked, you can proceed again by clicking on the Next button.
Click the Next button after selecting the features you want to
install. Another window will check the feature rules. Once every rule is
checked, you can proceed again by clicking on the Next button.
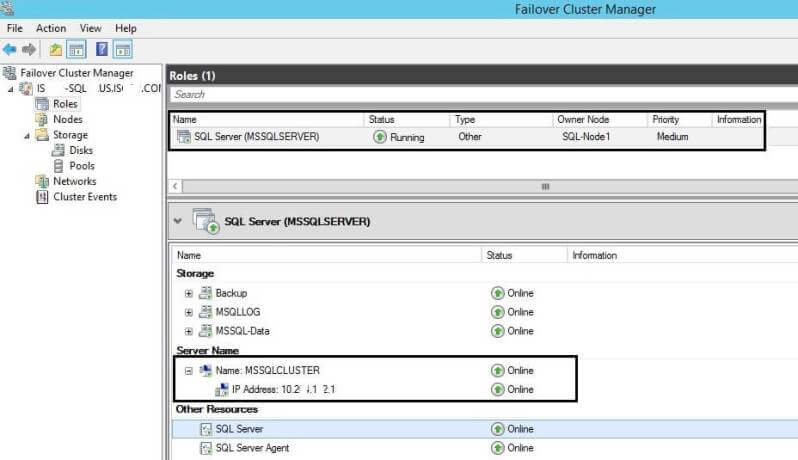
Step 8: Our next interface is the Instance Configuration window. This is an important step because in this step you enter the SQL Server Network Name along with the Instance ID. I have chosen "MSSQLCLUSTER" as network name and default instance (MSSQLSERVER) as the instance id. Now click on the Next button to go to the next window.
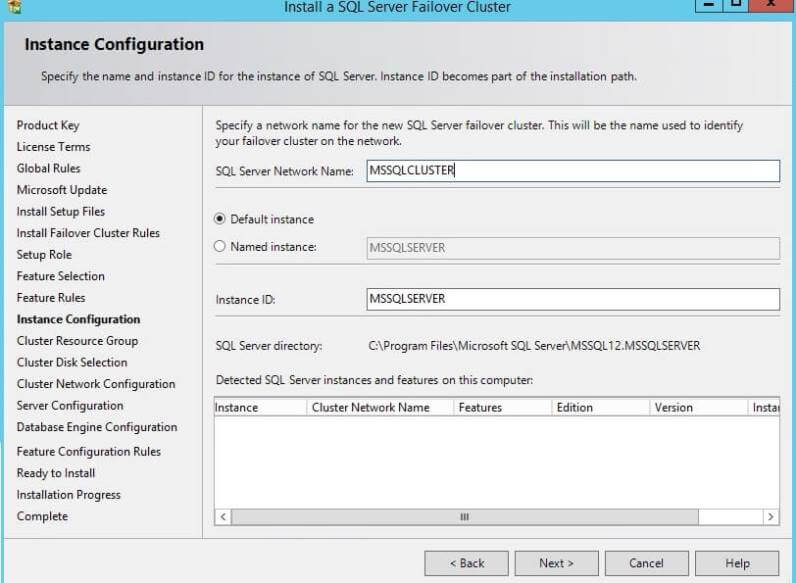 Step 9: Next window is for cluster resource group. You can
change the cluster resource group name, but I have kept it as and
clicked on the Next button to proceed.
Step 9: Next window is for cluster resource group. You can
change the cluster resource group name, but I have kept it as and
clicked on the Next button to proceed.
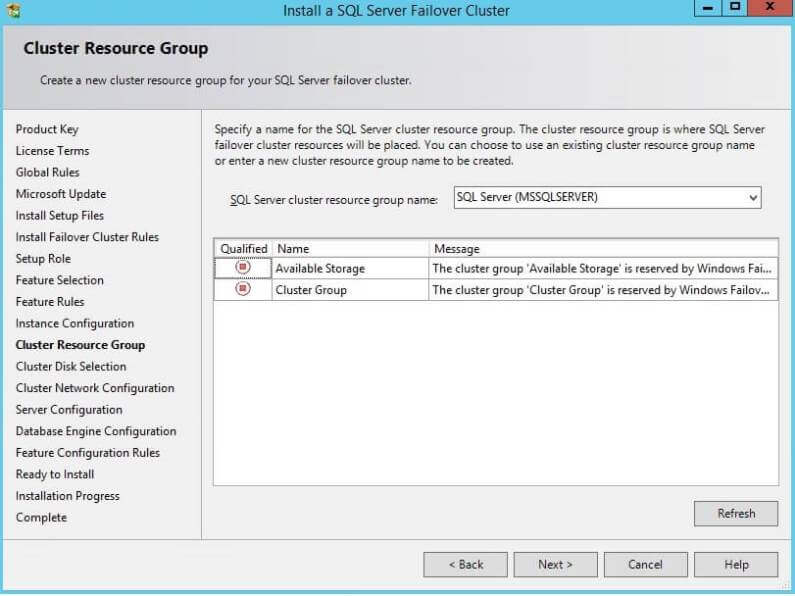 Step 10: The Cluster Disk Selection window is where you will
see the list of all shared disks that you can include in the SQL Server
cluster resource group. I have selected all three shared disks and
clicked on the Next button to proceed. If you have multiple shared
disks, make sure to select only those that will be part of this cluster.
Step 10: The Cluster Disk Selection window is where you will
see the list of all shared disks that you can include in the SQL Server
cluster resource group. I have selected all three shared disks and
clicked on the Next button to proceed. If you have multiple shared
disks, make sure to select only those that will be part of this cluster.
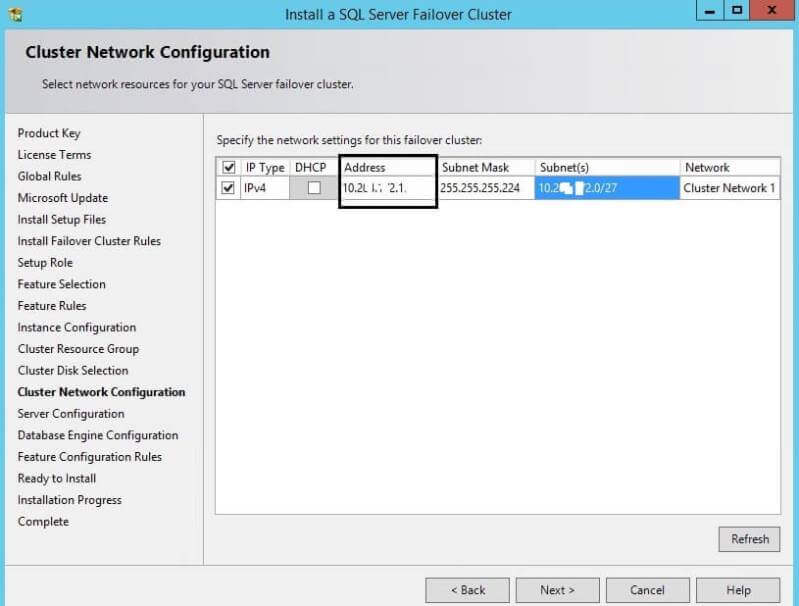
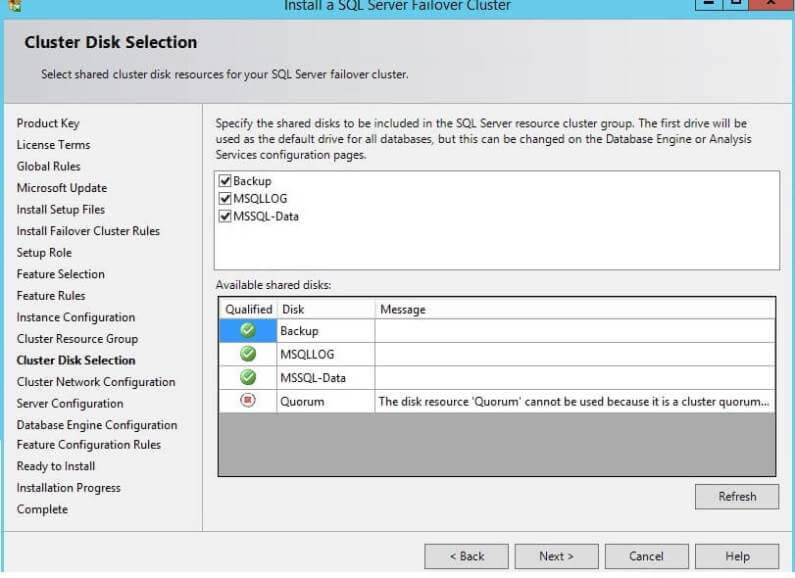 Step 11: Next window is to configure the cluster network. Here
you need to enter your unique and unused IP address in the address
column as shown in below screenshot. This is the same IP address which I
talked about in the beginning of this tip. Enter the IP address and
click on the Next button.
Step 11: Next window is to configure the cluster network. Here
you need to enter your unique and unused IP address in the address
column as shown in below screenshot. This is the same IP address which I
talked about in the beginning of this tip. Enter the IP address and
click on the Next button.
 Step 12: Once you click Next in the above step, it will ask
you to enter the SQL Server service accounts and their passwords to run
the SQL Server services. I used two service accounts, one for SQL Server
and another for SQL Server agent. Enter the credentials and click on
the Next button to go to the database engine configuration page.
Step 12: Once you click Next in the above step, it will ask
you to enter the SQL Server service accounts and their passwords to run
the SQL Server services. I used two service accounts, one for SQL Server
and another for SQL Server agent. Enter the credentials and click on
the Next button to go to the database engine configuration page.
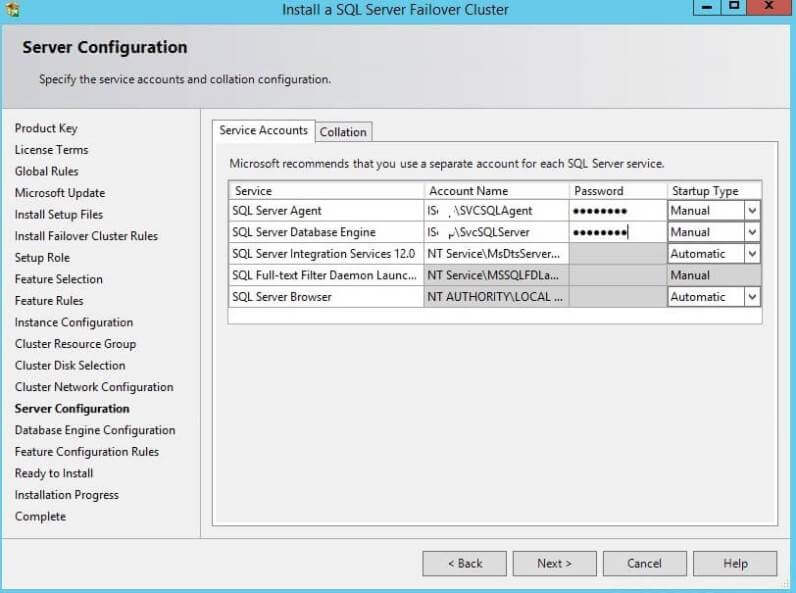 Step 13: Next window is very important and here setup will ask
you to configure the SQL Server database engine. There are three tabs
in this window. First is 'Server Configuration', second is 'Data
Directories' and third is 'FILESTREAM'. We will start configuring with
the first tab that is server configuration. The below screenshot
explains this window. We need to select the authentication mode of the
SQL Server. I have selected "Mixed Mode" and entered the sa password.
Make sure to enter a complex password otherwise it will not allow you to
proceed. Now click on "Add Current User" to add yourself as an
administrator on SQL Server. You can add other accounts as well which
should be admins in SQL Server.
Step 13: Next window is very important and here setup will ask
you to configure the SQL Server database engine. There are three tabs
in this window. First is 'Server Configuration', second is 'Data
Directories' and third is 'FILESTREAM'. We will start configuring with
the first tab that is server configuration. The below screenshot
explains this window. We need to select the authentication mode of the
SQL Server. I have selected "Mixed Mode" and entered the sa password.
Make sure to enter a complex password otherwise it will not allow you to
proceed. Now click on "Add Current User" to add yourself as an
administrator on SQL Server. You can add other accounts as well which
should be admins in SQL Server.
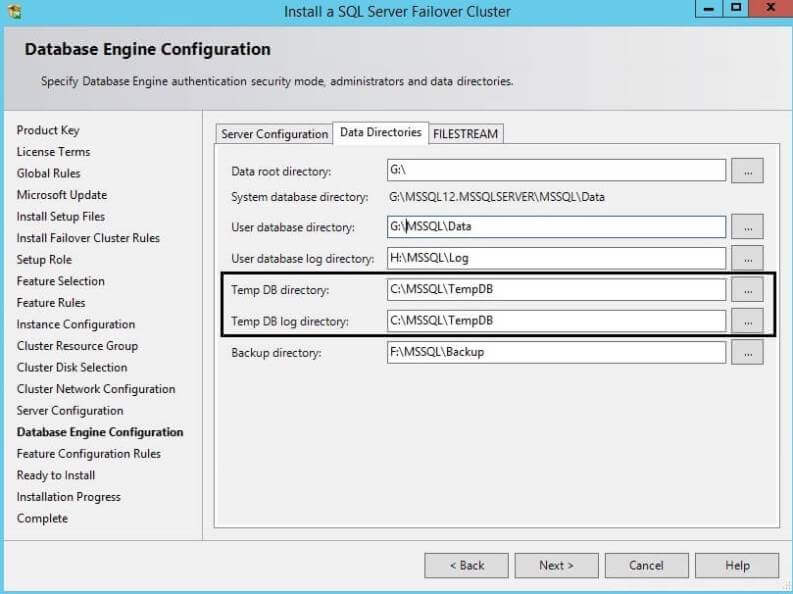
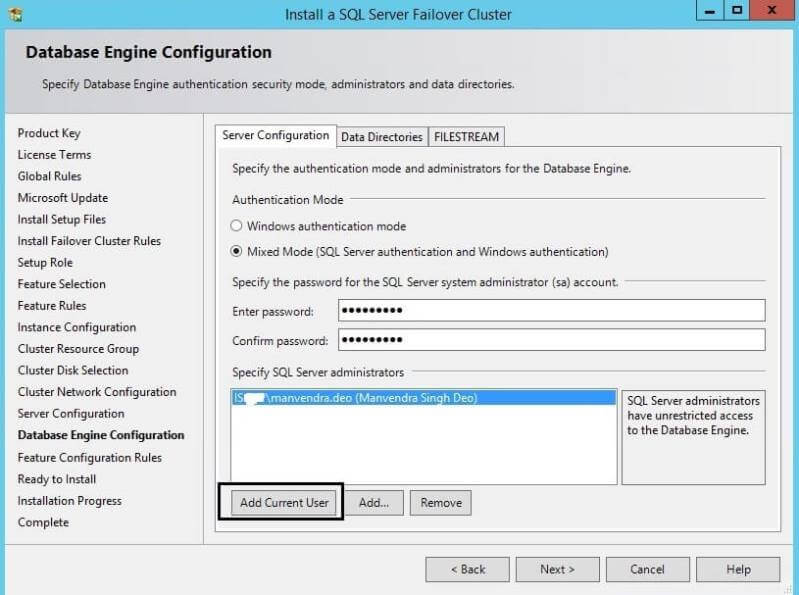 Now click on "Data Directories" to configure the data directories
where the system and user databases along with backup files will be
placed. I have placed system databases except TempDB, user databases and
backups on shared disks, but left TempDB on a local drive (C drive).
Now click on "Data Directories" to configure the data directories
where the system and user databases along with backup files will be
placed. I have placed system databases except TempDB, user databases and
backups on shared disks, but left TempDB on a local drive (C drive).
SQL Server failover cluster installation supports Local Disk only for installing the TempDB files. Make sure that the path specified for the TempDB data and log files exists on all the cluster nodes. If the TempDB directories are not available on the failover target node during failover, the SQL Server resource will fail to come online. Another advantage of placing TempDB on a local disk is that it creates separate paths of traffic by having your data and log files on the SAN while TempDB is on the local disk.
 I do not need FILESTREAM to be enabled, so I will not configure it
and click Next to proceed. If you need FILESTREAM click on the third tab
and follow the process to setup.
I do not need FILESTREAM to be enabled, so I will not configure it
and click Next to proceed. If you need FILESTREAM click on the third tab
and follow the process to setup.
Once you click Next, the below screen will appear to have you confirm that you are putting TempDB files on local drives.
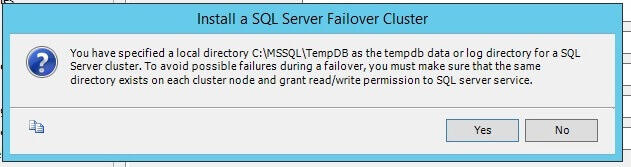 Click on Yes and it will check the configuration rules of this
installations. Once all rules have passed, click on Next to reach the
final installation screen.
Click on Yes and it will check the configuration rules of this
installations. Once all rules have passed, click on Next to reach the
final installation screen.
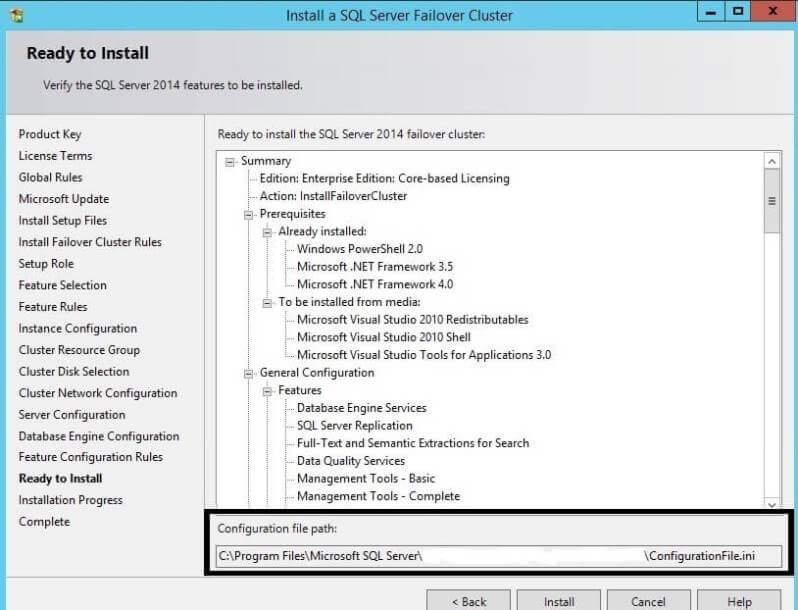
 Step 14: Here you can check the features and configurations
you have selected. You can also see the configurationFile.ini file in
the highlighted area that will be used by the setup to install SQL
Server.
Step 14: Here you can check the features and configurations
you have selected. You can also see the configurationFile.ini file in
the highlighted area that will be used by the setup to install SQL
Server.
 Now click on the Install button to start the installation process of
SQL Server. You can see the installation is running based on the
progress in the below screenshot.
Now click on the Install button to start the installation process of
SQL Server. You can see the installation is running based on the
progress in the below screenshot.
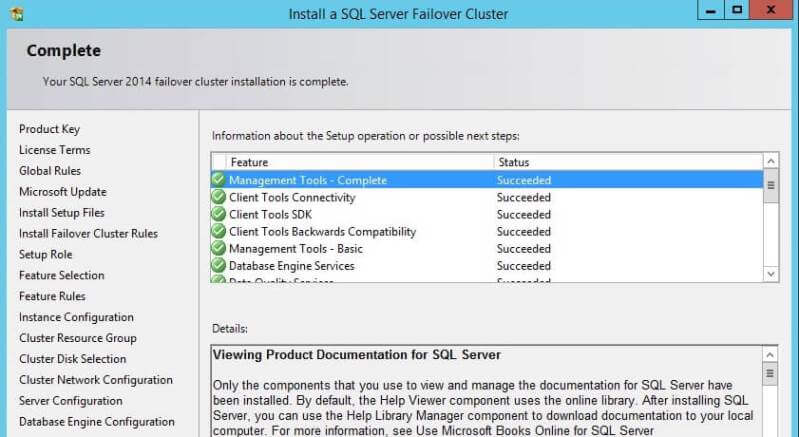
 Once the installation successfully completes, you will get the below
screen with confirmation that all the features you have selected are
installed.
Once the installation successfully completes, you will get the below
screen with confirmation that all the features you have selected are
installed.
SQL Server 2014 cluster Installation
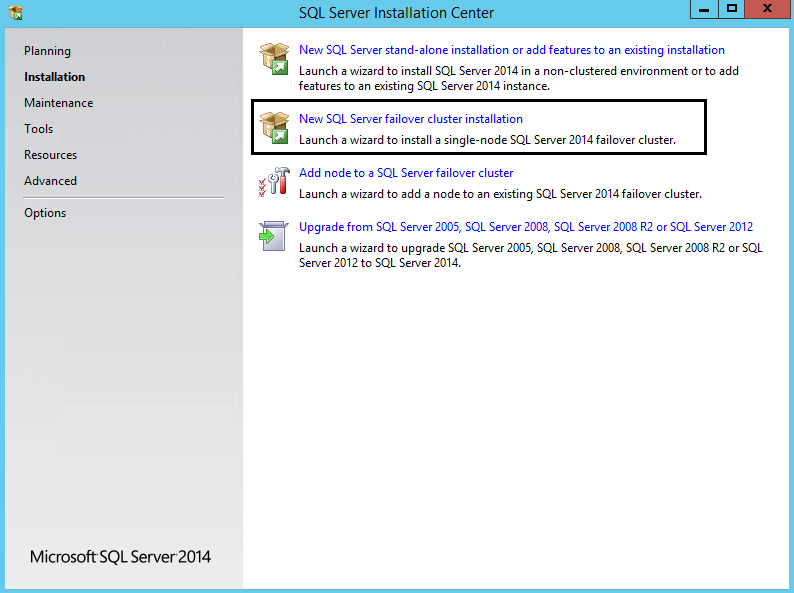
Step 1: Go to the SQL Server setup file location. Right click on setup.exe and choose "Run as administrator". The SQL Server Installation Center will appear on your screen as shown in the screenshot below. Select the "Installation" tab from the left pane and click on "New SQL Server failover cluster installation" from the right pane.
Step 8: Our next interface is the Instance Configuration window. This is an important step because in this step you enter the SQL Server Network Name along with the Instance ID. I have chosen "MSSQLCLUSTER" as network name and default instance (MSSQLSERVER) as the instance id. Now click on the Next button to go to the next window.
SQL Server failover cluster installation supports Local Disk only for installing the TempDB files. Make sure that the path specified for the TempDB data and log files exists on all the cluster nodes. If the TempDB directories are not available on the failover target node during failover, the SQL Server resource will fail to come online. Another advantage of placing TempDB on a local disk is that it creates separate paths of traffic by having your data and log files on the SAN while TempDB is on the local disk.
Once you click Next, the below screen will appear to have you confirm that you are putting TempDB files on local drives.
No comments:
Post a Comment